Rishubh Parihar
I am a final year PhD student at IISc Bangalore, advised by Prof. Venkatesh Babu. I work on developing methods to enhance controllability in vision generative models by designing interfaces beyond text to interact with these models.
I spent an amazing summer at Snap Research working on controllable image editing. Prior to my Ph.D., I gained industry experience at Samsung Research, where I developed face editing solutions for Samsung smartphones, and at ShareChat, focusing on multimodal algorithms for content moderation.
I obtained B.Tech from IIT Delhi in Mathematics and Computing, where I worked with Prof. Prem Kalra on synthetic makeup transfer.
[New] I am interested in an industrial full-time research position. Please feel free to connect.


Recent News
- [Feb 26]Kontinuous Kontext and SeeThrough3D accepted at CVPR 2026!
- [Sep 25]Awarded Outstanding Reviewer at ICCV 2025!
- [Jun 25]Our work on Zero-Shot Depth-Aware Image Editing with Diffusion Models accepted at ICCV 2025!
- [May 25]Awarded Outstanding Reviewer at CVPR 2025!
- [Apr 25]Awarded best presentation award at IISc EECS Symposium 2025, Visual Analytics Cluster.
- [Feb 25]Compass Control and MonoPlace3D accepted at CVPR 2025!
- [Nov 24]Our ECCV 2024 paper PreciseControl on personalization of T2I models was featured in Times of India.
Publications
2026


Kontinuous Kontext: Continuous Strength Control for Instruction-based Image Editing
CVPR 2026
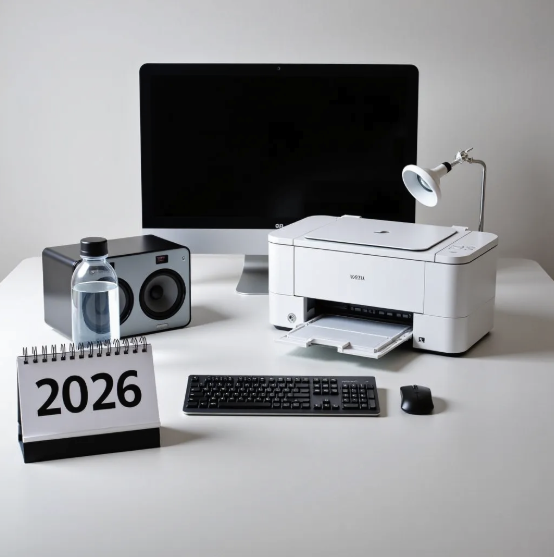

2025
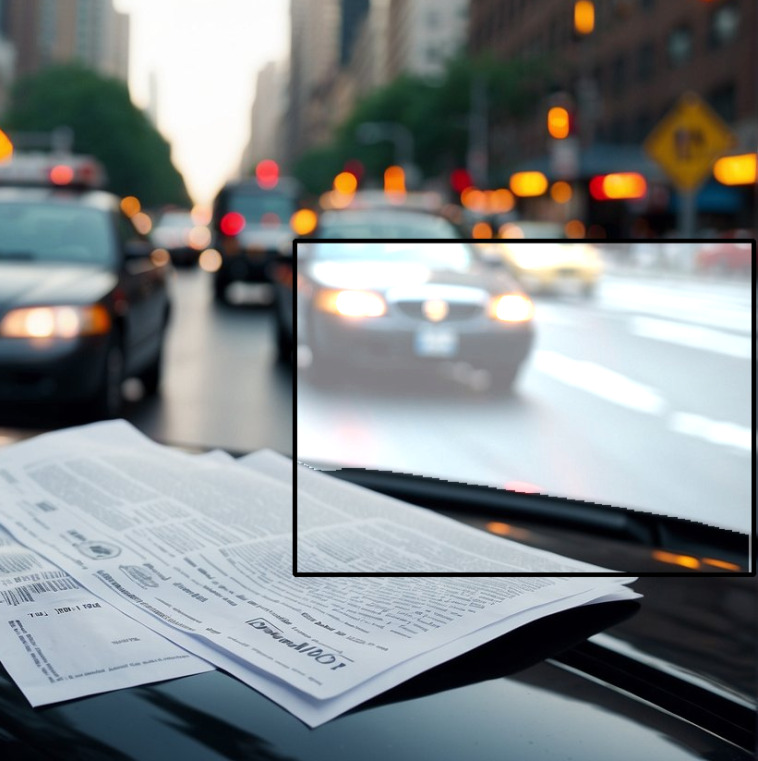
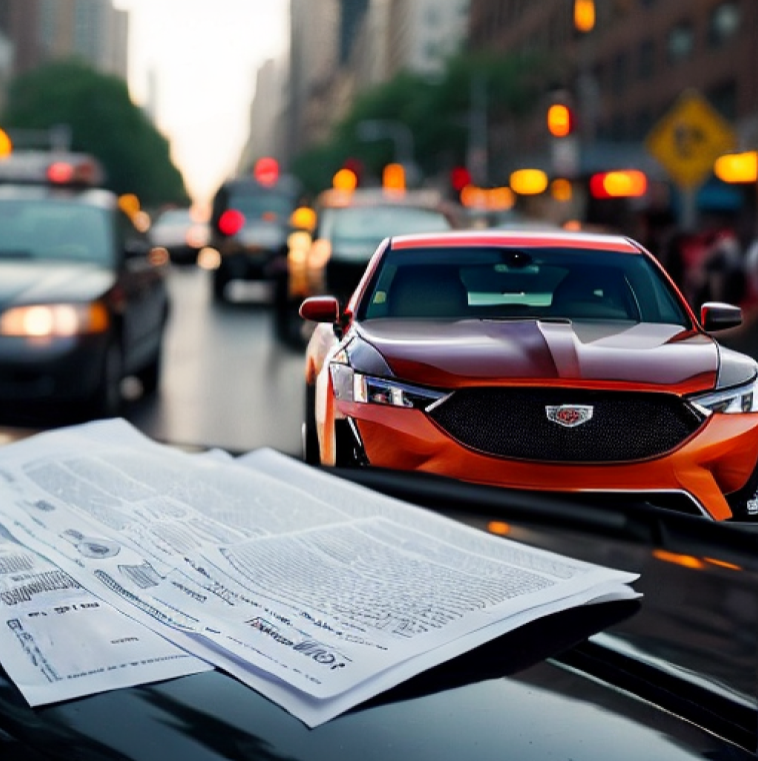
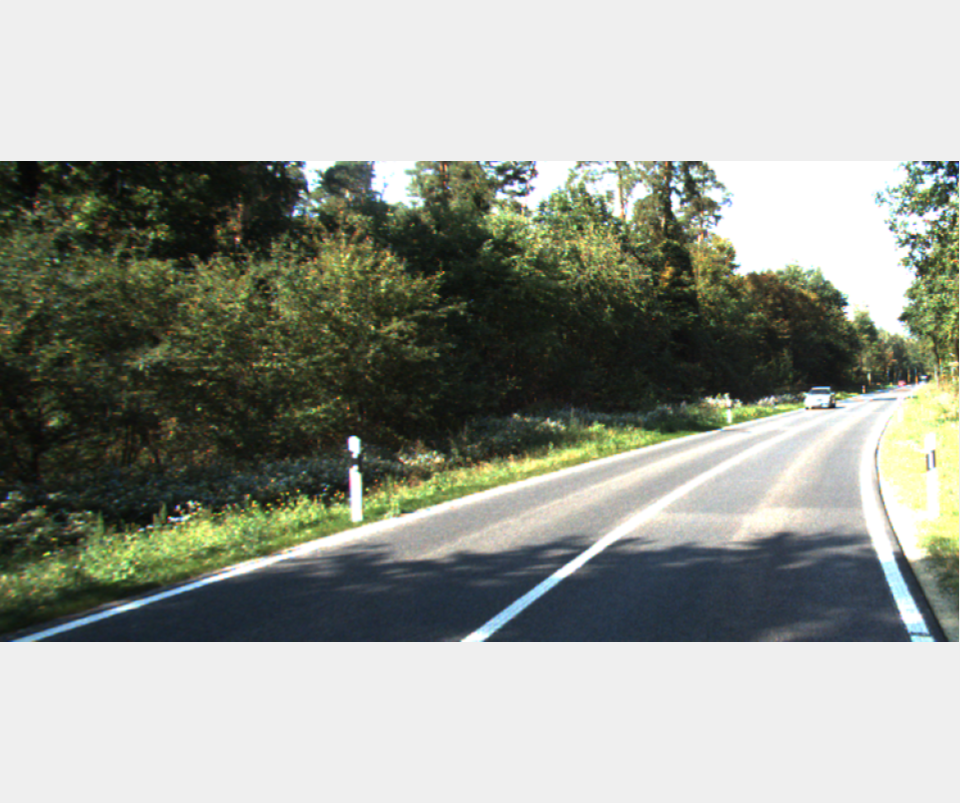
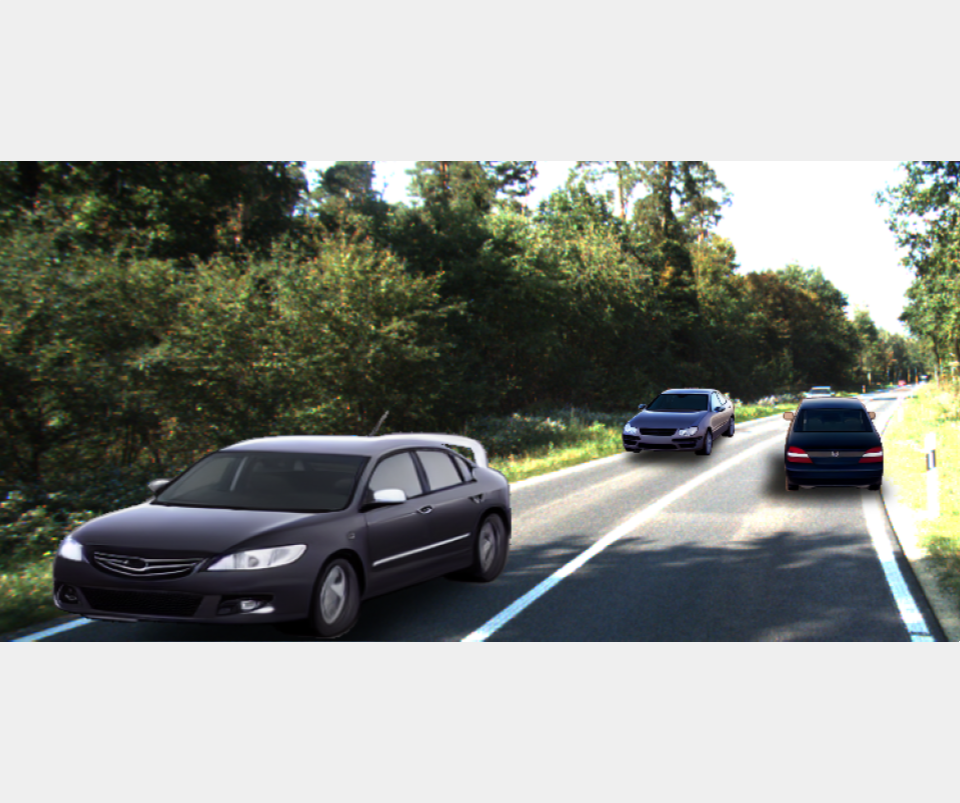




MonoPlace3D: Learning 3D-Aware Object Placement for 3D Monocular Detection
CVPR 2025


🧭 Compass Control: Multi-Object Orientation Control for Text-to-Image Generation
CVPR 2025


Reflecting Reality: Enabling Diffusion Models to Produce Faithful Mirror Reflections
3DV 2025


Attribute Diffusion: Diffusion Driven Diverse Attribute Editing
WACV 2025 (Workshop on Diffusion Models, NeurIPS 2023)
2024


PreciseControl: Enhancing Text-to-Image Diffusion Models with Fine-Grained Attribute Control
ECCV 2024
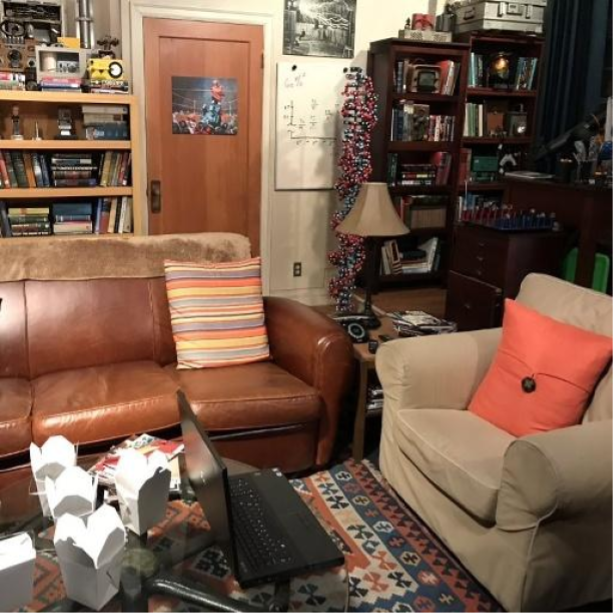
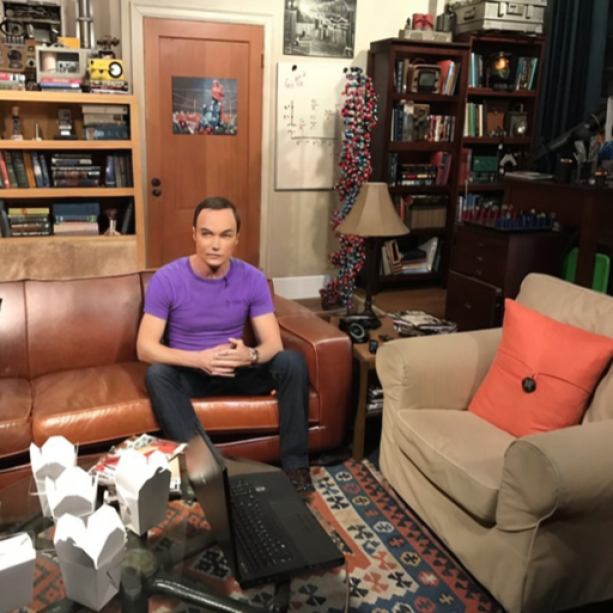




Balancing Act: Distribution-Guided Debiasing in Diffusion Models
CVPR 2024
2023




We never go out of Style: Motion Disentanglement by Subspace Decomposition of Latent Space
Workshop on AI for Content Creation, CVPR 2023
2022
Everything is in the Latent Space: Attribute Style Editing and Attribute Style Manipulation by StyleGAN Latent Space Exploration
ACM Multimedia 2022


Photography








Sketches